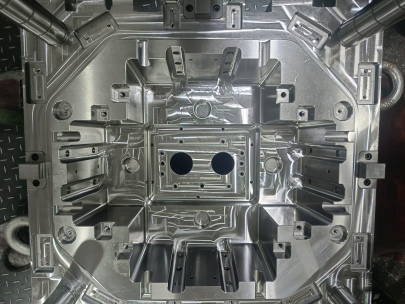
When it comes to manufacturing, the importance of selecting the right mould parts cannot be overstated. This Essential Guide aims to provide an insightful overview of the various components involved in mould making and how to select them based on your specific manufacturing needs. Whether you are venturing into plastic injection molding, blow molding, or any other method, understanding these components can significantly enhance your production efficiency and product quality.
Understanding Mould Components
Moulds are comprised of several key components, each serving a unique purpose in the manufacturing process. Here’s a breakdown of some of the primary mould parts:
- Mould Base: The foundational structure that supports all parts of the mould.
- Cavities: The hollow spaces within the mould that shape the final product.
- Core: A component that forms the internal features of a part.
- Runner System: The pathway through which molten material flows into the cavities.
- Ejector Pins: These are used to eject the finished part from the mould once it cools.
- Cooling System: Ensures the efficient heat removal during the moulding process.
Factors to Consider When Selecting Mould Parts
Choosing the right mould parts involves considering multiple factors.
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Material Compatibility | Select parts that are compatible with the type of material you will be using (e.g., plastic, metal). |
| Production Volume | High-volume production may require more durable mould parts to withstand repeated use. |
| Complexity of Design | More intricate designs may call for specialized components to achieve desired features. |
| Cost | Evaluate the total cost of ownership, including maintenance and replacement costs. |
The Importance of Material Selection
The choice of materials for mould components is critical as it directly affects the performance and durability of the mould. Here are some common materials used:
- Steel: Known for its strength and longevity, often used for high-volume production.
- Aluminum: Lightweight and good for prototype runs due to faster machining times.
- Brass: Excellent for inserts and low-volume parts due to its machinability.
- Plastic: Sometimes used for simple moulds or prototype parts.
Common Moulding Processes and Their Requirements
Different moulding processes necessitate particular characteristics in mould parts. Here’s an overview of several popular methods:
- Injection Molding: Requires precise cavity sizes and robust cooling systems.
- Blow Molding: Needs well-designed cores for hollow parts and efficient air channels.
- Compression Molding: Typically calls for less complex moulds and thicker materials.
- Rotational Molding: Demands durable moulds that can withstand high temperatures.
Maintenance and Care of Mould Parts
Proper maintenance is crucial for extending the lifespan and performance of mould parts. Here are several key maintenance practices:
- Regular cleaning to remove debris and ensure smooth operation.
- Frequent inspections to identify wear and tear early.
- Lubricating moving parts to reduce friction and prevent damage.
- Proper storage after use to avoid corrosion and environmental damage.
Innovations in Mould Technology
The moulding industry is continuously evolving with new technologies that enhance performance and quality. Here are some innovations to look out for:
- 3D Printing: Enables rapid prototyping and customisation of mould designs.
- Smart Moulds: Integration of sensors for real-time monitoring of temperature and pressure.
- Advanced Cooling Techniques: Ensures consistent cooling, reducing cycle times significantly.
Conclusion
Choosing the right mould parts is a crucial step in optimizing your manufacturing processes. By understanding the various components, considering material and design factors, and ensuring proper maintenance, you can significantly enhance production efficiency and product quality. As the industry moves towards more advanced technologies, staying informed about innovations can provide a competitive edge. Remember, the right combination of mould parts tailored to your unique manufacturing needs can lead to substantial improvements in both output and profitability.